
The first alloy glass metal was made of glass and silicon, which was tested and produced in 1960 at the California Institute of Technology. These metals were produced by rapid cooling (megaclevin per second), which prevents the formation of a crystal structure.
In 1969, glass metal alloys containing 77.5 percent palladium, 6 percent copper, and 16.5 percent silicon were made with relatively low critical cooling rates.
A group of metals that have an irregular atomic structure. So this irregular atomic structure is like the structure of glass. Most metals have a solid crystalline structure.
Unlike glass, they have poor crystal conductivity due to their crystalline structure. On the other hand, these metals have very good electrical conductivity. There are various methods for producing these metals, including very rapid cooling, solid state reaction, ion irradiation, and mechanical alloying.

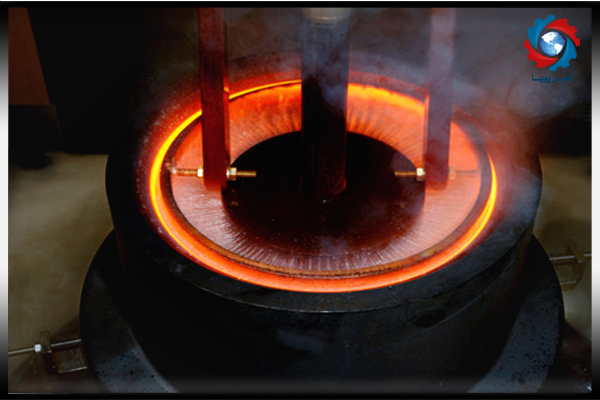
Melting of alloys and metals is usually done at very high speeds and high temperatures. For this purpose, there must be a material with a very low thickness to be able to create a high quenching speed.

In this method, amorphous solids that have the same and similar physical properties and structure are obtained from the solidification method very quickly. The production of glass metals by this method dates back to Germany in the 1950s, when atoms were deposited surface-by-surface and one-by-one.
To use this method, they often use volatile gases such as metal chlorides, metal fluorides, metal carbonyls, etc. When these gases are reacting inside a chamber, the reaction of these gases creates a metal vapor and a vapor component, which can be used to vaporize the sediment surface.
Glass metals have various applications, the most important of which are:
1. Can be used as a soft magnet
2. Coating material for soldering
3. Reinforcing fibers
4. Mechanical applications
5. Strengthening all types of polymer composites
6. Making all kinds of glass
7. Can be used in making all kinds of ceramics
.jpg)
Metal alloys that are relatively light and have high specific strength and good corrosion resistance can be produced by amorphous alloys based on aluminum and magnesium. Transition and Ln is a lanthanide metal).
It can be said that the highest tensile strength is 1330 MPa for aluminum base alloys and 830 MPa for magnesium base alloys. In addition, magnesium-based alloys have a very large capacity to form glass (amorphous) phases, which are produced by high-pressure injection molding (die-casting).
Extrusion of amorphous aluminum-based powders at temperatures above the crystallization temperature results in high-strength materials with a fine structure of intermetallic compounds dispersed in the aluminum substrate.
In this case, the highest values of tensile strength and fatigue limit are 940 and 313 MPa, respectively. An extruded alloy of Al-Ni-MM (which is MM ewe metal) has already been used for machine parts and further development of commercial structural materials is expected from this alloy.

Ahan Pouya with more than a decade of best-selling experience, adheres to professional and ethical principles in the field of selling and buying at inside and outside the borders of Iran, helping you in the steel industry.