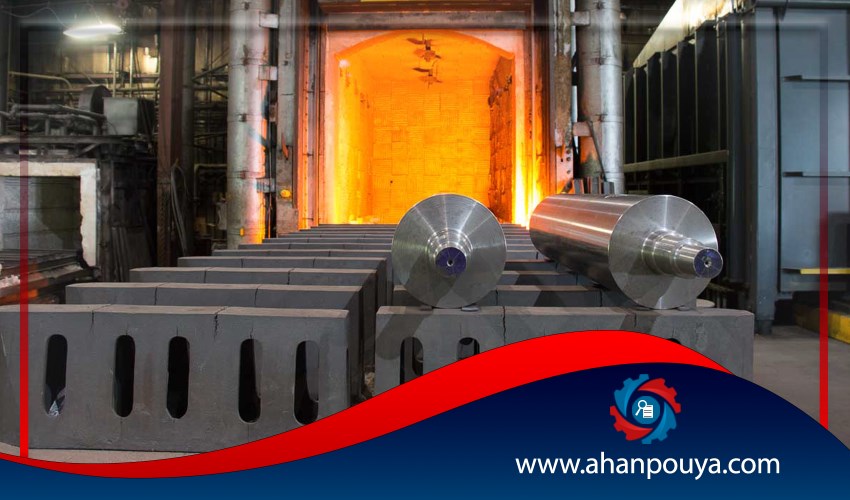

In different industries we need parts that have good toughness as well as having a hard surface . Using heat treatment in order to increase the hardness level of the component is called hardening .
Metal hardening is one of the main steps in manufacturing most industrial components . As the name suggests , it becomes harder to accomplish by doing it . Mechanical properties will be improved by using the operation , as well as increasing the surface hardness of the component .
By doing hard heat treatment , the pieces become more durable and lasting . The alloys heated to a temperature more than the critical transformation temperature , then quickly chill to a certain extent to make the metal structure very tough .

According to the amount of alloying elements in materials , the alloys can be cooled by air or by drowning in oil , water or other liquids . Hardening materials usually lose their temper , which is suitable for improving dimensional stability and increasing toughness .
Steel components often require a heat temperature and metal hardening operation to obtain improved mechanical properties such as increased toughness and strength .
Hardening is called a process in which the surface of steel is changed and mechanical , metallurgical , chemical and physical properties of steel can be changed and improved , but it’s internal part will not change and can be used in manufacturing industrial components .
Steel is an alloy made by combination of iron and carbon . Steel heats and cools during an alternative process . This process is called hardening and it will change the mechanical properties of steel . Some of these changes will be mentioning below :
- Machining improves .
- Improving magnetic properties .
- Improving electrical properties .
- Increasing the resistance against erosion by creating a crystal layer on surface .
- Removing the remained stress .
- Increasing the energy absorption .
- Increasing stiffness and increasing impact resistance .
- Improving cut properties .
● Hardening process is due to the fact that in the manufacturing of industrial components , for example , production of gear, crankshaft , and so on steel is required to reach a higher hardness level so that it can withstand the pressure exerted during application and be resistant to the damages and toughness .
Cooling has an outstanding disadvantage . Cooling speed is so high , therefor it is possible to create some bending or distortion in this method . Other methods are possible to hardening metals so that these defects remove , and needed properties obtain . The methods are :
1. Quenching
2. Hardening with self-tempering
3. Stepped quenching or martempering
4. Isothermal quenching or austempering
● Next in this article we will discuss about mentioned methods .
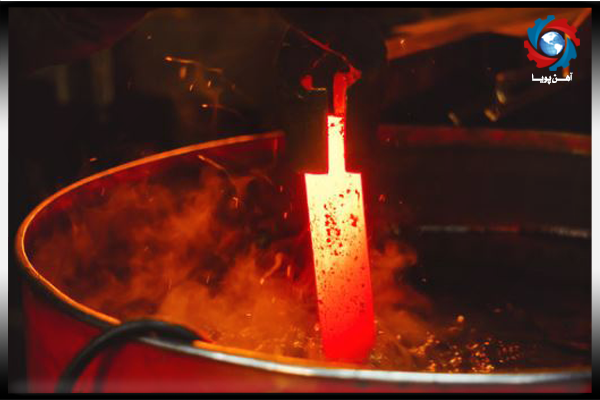

In quenching first the molten materials cooled in the water ( in temperature between 300 to 400 ° ) and transferred immediately to a cooler place ( such as air or oil ) with less density and remained there to become completely cold .
The most important reason to operation of 2nd quenching is to lessen the interior stresses and changing the form of austenite to martensite .
In this method first it doesn’t cool down in water or oil immediately ; because it may cause the austenite minor decomposition in 500 to 600 ° and create remained stresses causing fast cooling .
In this method , materials are kept in a cooling place until it is completely cooled .
The metal must be removed at the right time to maintain a certain amount of heat within its core . This reduces heat . In addition , the appropriate time to interrupt cooling should be tested .
In this method , more heat than that required for cooling is maintained in the core, and by reaching the suitable temperature , the material will be immersed in the cooling liquid .
This method is applied to instruments that are hard to surface with hard core . Some of these instruments are :
- Chisels
- Sledge hammers
- Manual hammers
- Central staplers
Martempering
Martempering is after heating the steel to a hardened temperature , it is cooled in an environment with temperatures ranging from 20 to -20 ° c .These materials are kept until they reach the ambient temperature and then to reach room temperature in the air and sometimes in cold oil .
The maintenance time in the silencer should be enough to obtain the degree of uniformity in the cross-section .
But it should be noted that , this time should not be too long to cause austenitic decomposition . The austenite ( solid solution of carbon in iron ) is converted to martensite during the subsequent cooling period . Martensite is an unstable metal which creates by cooling of the austenite steel .
Ausetempering is mainly done in the same manner with martempering but in order to ensure the dissolution of the austenite , the longer holding time in both hot temperatures ( above the martensite point ) is performed . Evidences show that the use of steam in many grades of steel can significantly increase the structural strength .
In comparison with normal hardening and temperature adjustment at -80 ° c , the austempering method reduces the cut – off from the center and can double the shaping of iron .
However , it should be noted that hardening with cooling in a hot environment is not suitable for all levels of steel and for all sizes . In addition , choosing an unsuitable method may have some disadvantages like mechanical properties may decrease considerably .
Molten salt is usually used as a medium for production and extraction . The higher temperature , the greater the cooling rate .
Since cooling in molten salt is only achieved by conduction, the cooling capacity increases considerably .
Austempering process is used commercially for thin steel sections to obtain products free of crack and resistance to impact .
In different industries we need parts sometimes that have good toughness as well as having a hard surface .
The meaning of toughness is the ability of the materials to resist energy absorption and non-deformation . Using heat treatment in order to increase the hardness level of the component is called hardening .
Hardening is the latest process done in order to increase the surface strength of the materials .
This type of thermal treatment allows the pieces to have hardness and resistance and increase the mechanical properties both .
● Hardening is used to produce some industrial components such as gear and crankshaft .
The temperature required for thermal treatment is dependent on the type of steel alloy and the size of the component .
The smaller the size of the steel piece , the temperature will reduce . Martensite causes hardness and resistance against wear increase . Maximum steel hardness is shaped when martensite structures totally confirm .
To create this martensite structure , the samples should be cooled as fast as possible . Water or oil is used for cooling.

Ahan Pouya with more than a decade of best-selling experience, adheres to professional and ethical principles in the field of selling and buying at inside and outside the borders of Iran, helping you in the steel industry.